
\[ \]
\[ \]
\[ \]
Issue No 18, 27 February 2023
By: Anthony O. Ives
Electric power is being pushed as the future at least at the time of writing that was the case. The argument is that its more environmental friendly primarily by reducing CO2 emissions. Whether you believe that argument does not really matter because political legislation at the present time is pushing us toward electric powered vehicles so it could be the case that we will come more dependent on electric power in the future. Electric power is also the most convenient way to power small UAVs. Batteries are one option for storing and delivering power to electric powered vehicles the other is fuel cells. Batteries and fuel cells are closely related in working principle.
Batteries and fuel cells are based on the principle of electrolysis, that a chemical reaction produces a electric voltage. In some cases an electric voltage can also reverse the chemical reaction. More details of electrolysis can be found in Ref [1]. The difference between batteries and fuel cells is whether the chemicals are contained or not. In batteries almost all of the chemicals stay contained with in the battery container, some chemicals may leak, evaporate, etc but the vast majority stays contained. A battery will continue to produce a electric voltage until all the chemicals have reacted. In some batteries the chemical reaction is reversible by apply a voltage across to the batteries these type of batteries are rechargeable. If the chemical reaction is not reversible then the battery is non rechargeable. Fuel cells produce electric voltage by flow of chemicals which react with each other. Using a hydrogen fuel cell as an example, hydrogen is stored in a fuel tank and oxygen is taken from the atmosphere so it operates in a similar way to an internal combustion engine only the chemical reaction is not producing heat and then mechanical movement but an electrical voltage. In the case of a hydrogen fuel cell a reverse fuel cell operation (or electrolysis) would produce hydrogen and oxygen from water, hydrogen and oxygen react together to produce water. For this reason hydrogen is also thought to be a future energy resource at least at the time of writing. Excess energy from renewables such as wind power could be used for electrolysis of water to produce hydrgen hence effectively storing energy from renewables that cannot be used immediately. For more on hydrogen and fuel cells see Ref [2]. The chemical reaction for hydrogen fuel cells is given below:
2H++O-<=>H2O (Water)
Electrolysis can be very basically discribed as a liquid solution with two metal rods (or an electrically conducting material) placed in it called electrodes. Each battery terminal connecter is connected to an electrode. The electrode connected to the positive terminal is called an anode, the negatively charged ion called an anion is drawn to it. The other electrode connected to the negative terminal is called a cathode, the positive charged ion called a cation is drawn to it. In the electrolysis of water the hydrogen ion, H+ is the cation and the oxygen ion, O+ is the anion. This is a very basic description of electrolysis for a more detailed description see Ref [1] and [2]. The picture below gives a graphical description of an electrolysis set up.
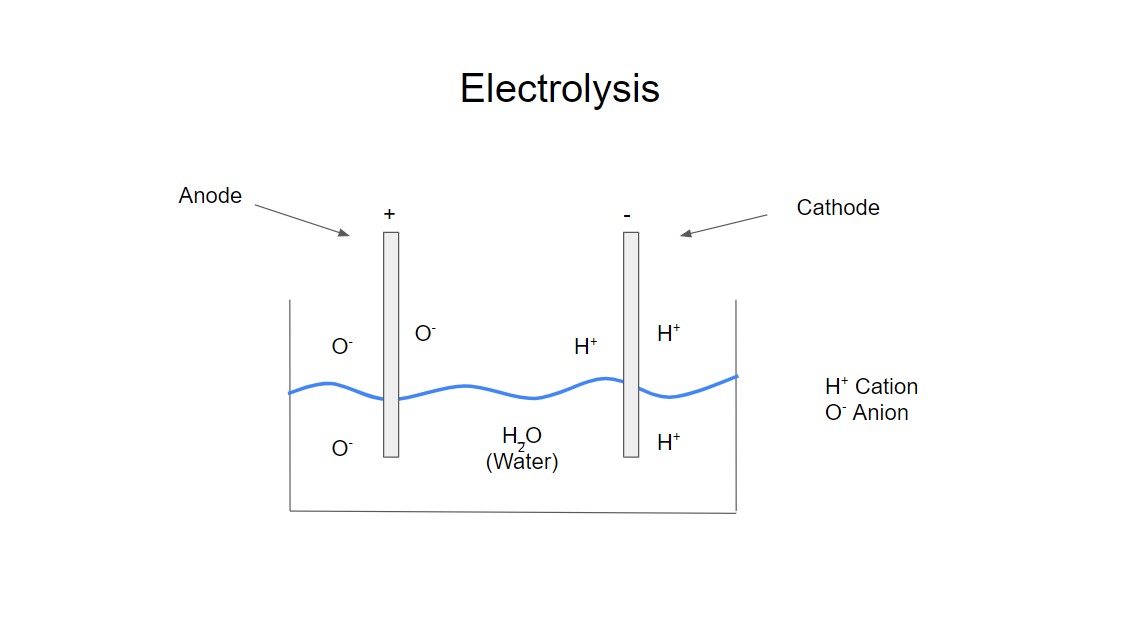
The basic principle of electrolysis will be similar in batteries but how it actually looks could be a lot more complicated. Lead acid batteries were reasonablely simple and very similar to the basic description of electroylsis giving in this article however lithium ion and lithium ploymer battries are more complex. Lithium ploymer batteries enabled electric model aircraft to achieve the same performance that previously only models with internal combustion engines could achieve. Lithium ploymer batteries give higher performance with a lot lower weight, however they require more care and can be dangerous if mishandled, so as some one once said with great power comes great responsibility. Older less powerful batteries such as NiCads were more robust and could take more abuse. Lithium ploymer batteries become unstable if their voltage falls outside the recommended range, you can also get explosive results if you puncture them. So it is recommended to read the manufacturers instructions on how to operate them and use the correct charger and equipment with them. This article does not intend to give a detailed description of battery technology just more of a brief overview. A comparison of battery properties and for more discussion see Ref [3].
This article is a good place to introduce some basic electrical principles and these are basic principles. A basic circuit consists of a power source typically a battery and a resistor. The diagram below shows the most basic electrical circuit possible.
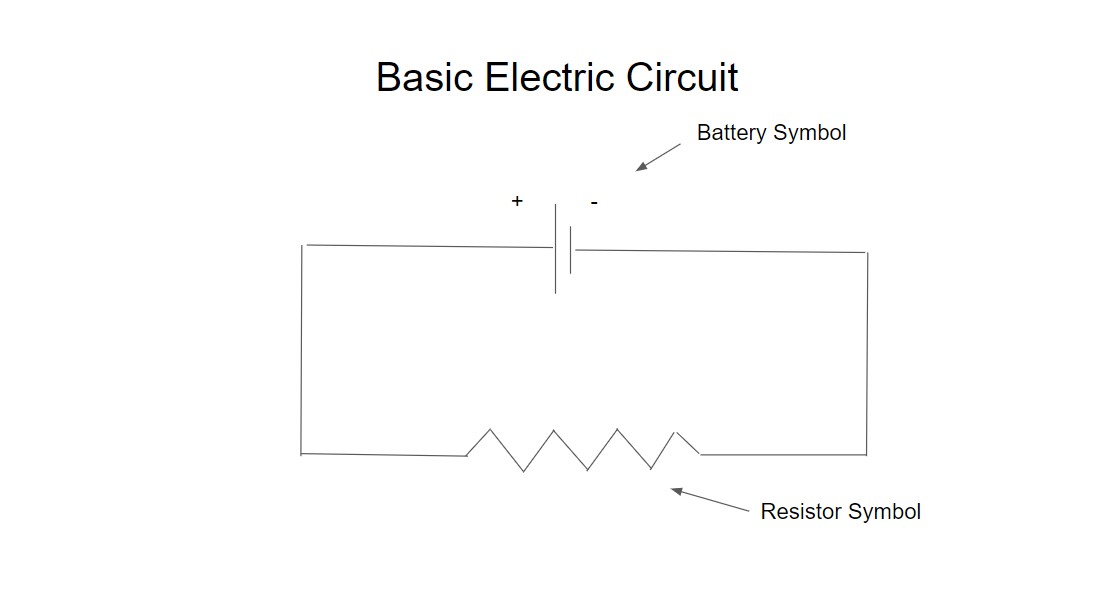
The resistor is representative of any electrical resistance in the circuit such as the conducting wire or a specific electronic resistor or combination of both. The voltage which is also known as the electric potential difference drives an electrical current round the circuit. The equation below describes this relationship mathematically and more precisely:
V =IR
Where V is voltage or electric potential diffence, I is electric current and R is resistance.
Electrical power is defined by the following equation:
P=VI
This type of circuit would be typical for an electric light however for one with an electric motor the circuit would involve more complex electric principles which could have a different value for current however electric power can still be derived using the same equation if the correct current is used. Voltage is usually based on what the battery can provide while current is usually based on what voltage can be supplied and the electric components that are in the circuit.
Future articles will discuss how batteries charge and discharge as well as the effect of electric motors on electric current and power, Ref [4] is a good reference for finding out more about and understanding electric principles.
Please leave a comment on my facebook page or via email and let me know if you found this blog article useful and if you would like to see more on this topic. Most of my blog articles are on:
Mathematics
Helicopters
VTOL UAVs (RC Helicopters)
Sailing and Sailboat Design
If there is one or more of these topics that you are specifically interested in please also let me know in your comments this will help me to write blog articles that are more helpful.
References:
[1] A-Level Chemistry, E. N. Ramsden, 3rd Edition, 1994, Nelson Thornes
[2] Hydrogen and Fuel Cells, Bent Sorensen, 1st Edition, 2005, Elsevner Academic Press?
[3] http://www.eiteog.com/EiteogBLOG/No3EiteogBlogMass.html
[4] Hughes Electric Technology, Edward Hughes, 7th Edition, 1995, Prentice Hall
Disclaimer: Eiteog makes every effort to provide information which is as accurate as possible. Eiteog will not be responsible for any liability, loss or risk incurred as a result of the use and application of information on its website or in its products. None of the information on Eiteog's website or in its products supersedes any information contained in documents or procedures issued by relevant aviation authorities, manufacturers, flight schools or the operators of aircraft, UAVs.
For any inquires contact: [email protected] copyright © Eiteog 2022